Learning-Linux
Learning linux commands and shell scripting!
This project is maintained by Curovearth
PART 1: Introduction to Linux
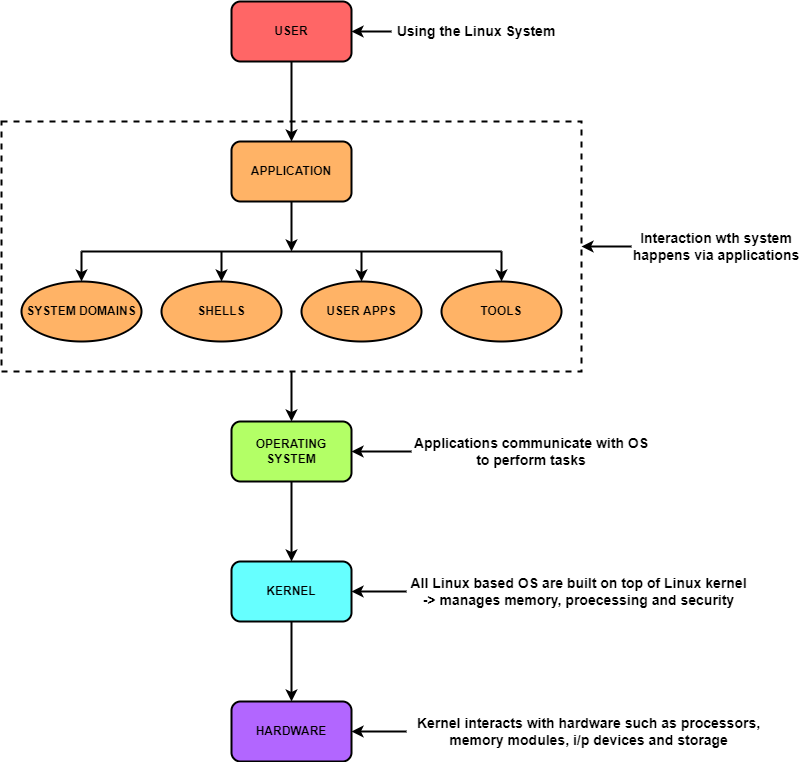
LINUX Architecture
Important Directories
| Directory | Contains |
|---|---|
/bin |
Sytem libraries |
/sbin |
Binaries that require root privileges |
/usr |
User programs and data |
/home |
Home directory |
/media |
Removable media device directories |
Creating and Editing Files
- We do this with the help of a variety of command-line or GUI-based text editors.
- gedit is a GUI-based editor that provides many features to simplify your work
- GNU nano is a command line editor that provides similar functionality in a command line format
GNU nano Commands
sudo nano <filename>
Example
- Working in the folder:
cd /home/project - create a file:
nano myprogram.py - type the following in the file:
print("Learning linux is fun!") - Press
Ctrl+Xto exit - Press
yto save and then pressEnter - You should now be back at the terminal command prompt
- Run the python file:
python3 myprogram.py
VIM Commands
sudo vim <filename>- To insert text press
i - Press
ESCkey and type:wqto save a file and exit - Press
ESCkey and type:wto save without exiting - If you have made some changes which you need to discard
:q!
Installing Software and Updates
Deb and RPM packages
- deb and RPM formats are equivalent. so the contents of the file can be used on other types of Linux OSs.
- If a package is only available in one format you can use alien to convert it:
- RPM to deb:
alien <package-name>.rpm - deb to RPM:
alien -r <package-name>.deb
- RPM to deb:
Updating deb-based Linux
- Command line:
aptsudo apt update: to find available packages for your distrosudo apt upgrade: to install packagessudo apt upgrade <package-name>: for installing specific package
Updating RPM-based Linux
- GUI tool: PackageKit
- notifies you when updates are available
- lists available software updates
- Command Line tool: yum
- yum: yellow-dog updater modified
sudo yum update- gives a summary of all the available packages
- asks to confirm the download
Installing new software
- Installing a deb package with apt:
sudo apt install <package-name>
- Installing an RPM package with yum:
sudo yum install <package-name>
Summary 📝
- .deb and .rpm are distinct file types used by package managers in Linux operating systems
- deb and RPM formats can be converted from one to the other
- Update Manager and PackageKit are popular GUI-based package managers used in deb- and RPM-based distros, respectively
- And apt and yum are popular command line package managers used in deb- and RPM-based distros, respectively.
Quick Recap
- Linux originated in the 1990s when “Linus Torvalds” developed a free, open source version of Unix Kernel
- Linux distros differ by their UIs, shell, applications, and how the OS is supported and built.
- Popular linux distros
- RHEL: Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Debian
- Ubuntu
- Suse(SLES, SLED, OpenSuse)
- Fedora
- Mint
- Arch
- You can use a variety of command-line or GUI-based text editors such as GNU nano, vim, vi, and gedit.
- Deb and RPM packages contain software updates and installation files.
- You can use GUI-based and command-line package managers to update and install software on Linux systems.
Have Fun …